

Systems interaction failures are a source of security vulnerabilities. Four types of system integration errors are described. The integration of systems of systems, as well as technologies such as web services, change some of the design assumptions for security. The usage and characteristics of large systems or systems of systems raises analysis issues that may not be addressed by existing techniques. Software issues that arise if we maintain that separation are discussed this section. The expanded system scale that we can achieve with software integration also challenges the historical separation of systems and software engineering.

A successful attack on a system can indirectly affect systems that exchange information with the exploited system and particularly those that assume a trusted relationship with that system.ĭivide and Conquer - Software and Systems Engineering. Vulnerabilities can result from unanticipated interactions among systems or among systems, users, and system operators. Systems vulnerability analysis can require different techniques than those used to analyze source code and components for vulnerabilities. ” The scale that may be encountered in new systems can fundamentally change how system security is addressed in system development. The theme for the 2007 International Conference on COTS-Based Software Systems (ICCBSS) was “Systems’ Composition and Interoperability – A World in Transition.” The title of Steve Esterbrook’s 2007 keynote address was “Scale Changes Everything: Understanding the Requirements for Systems of Systems. Techniques to compose subsystems in ways that contribute directly to trustworthiness are, therefore, needed. In addition, NISs are generally developed and deployed incrementally. Thus, testing subsets of a system cannot adequately establish confidence in an entire NIS, especially when some of the subsystems are uncontrollable or unobservable, as is likely in an NIS that has evolved to encompass legacy software. NISs pose new challenges for integration because of their distributed nature and the uncontrollability of most large networks.
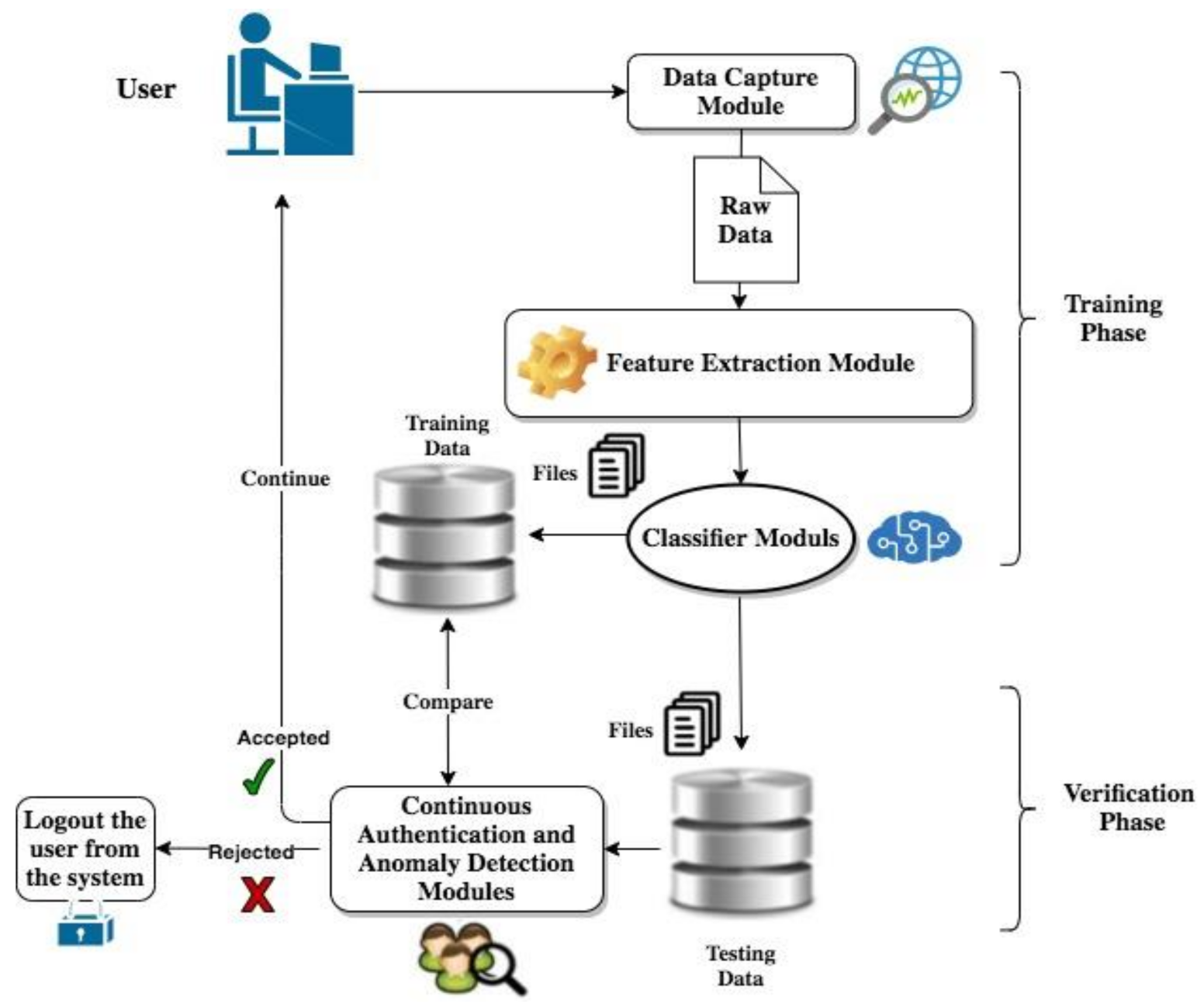
The following quote from Trust in Cyberspace notes the difficulty for solving some of the integration problems associated with deploying networked information systems (NISs) :


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
